- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
20. May 2018
The U.S. Pharmacopeia defines excipients as substances other than the active pharmaceutic ingredient (API) that are added in a drug delivery system in order to aid in the manufacturing process and enhance stability, bioavailability, safety, effectiveness and delivery of the drug. These substances have been appropriately evaluated for safety (1). Although excipients are well characterized and evaluated for safety, they can interact with the API chemically or physically (2). An incompatibility...
03. May 2018
The U.S. Pharmacopeia defines excipients as substances other than the active pharmaceutic ingredient (API) that are added in a drug delivery system in order to aid in the manufacturing process and enhance stability, bioavailability, safety, effectiveness and delivery of the drug. The 1968 phenytoin intoxication outbreak in Brisbane, Australia, is a classic example of an API-excipient interaction. When administered with CaSO4 the absorption of phenytoin was reduced due to an interaction between...
05. March 2018
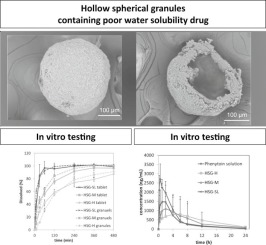
Water-soluble polymers with high viscosity are frequently used in the design of sustained-release formulations of poorly water-soluble drugs to enable complete release of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract. Tablets containing matrix granules with a water-soluble polymer are preferred because tablets are easier to handle and the multiple drug-release units of the matrix granules decreases the influences of the physiological environment on the drug.
10. June 2015
Lakmini Widanapathirana , Swapnil Tale , and Theresa M. Reineke * Department of Chemistry, University of Minnesota, 207 Pleasant Street SE, Minneapolis, Minnesota 55455-0431, United States Mol. Pharmaceutics, Article ASAP DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00202 Publication Date (Web): June 5, 2015 More