- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
13. September 2018
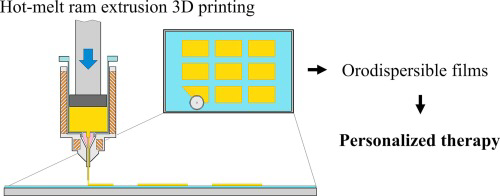
This work demonstrates the feasibility of the extemporaneous preparation of maltodextrins orodispersible films (ODF) by hot-melt ram-extrusion 3D printing. This method consists of three simple technological operations which can be also implemented in a pharmacy setting. First, maltodextrins, drug, and other excipients are mixed in a mortar and wetted with the plasticizer (i.e. glycerine). Then, the mixture is fed in the chamber of the ram-extruder and heated. ODF are individually printed on the...
25. February 2017
Abstract Punch sticking is a frequently occurring problem that challenges successful tablet manufacturing. A mechanistic understanding of the punch sticking phenomenon facilitates the design of effective strategies to solve punch sticking problems of a drug. The first step in this effort is to identify process parameters and particle properties that can profoundly affect sticking performance. This work was aimed at elucidating the key material properties and compaction parameters that influence...
15. June 2016
Context: The negative impact of magnesium stearate on the hardness of tablets is a well-known phenomenon, but the influence of paddle movement in the forced feeder on the lubricant effect during tablet compression is often neglected. Objective: The purpose of this research was to investigate the influence of paddle speed in the forced feeder on tablet tensile strength. Materials and methods: Mixtures of microcrystalline cellulose and magnesium stearate (0.5%) were blended using different...
04. June 2016
A full factorial design of experiments was used to study the effect of blend shear strain on the compaction process, relative density and strength of pharmaceutical tablets. The powder blends were subjected to different shear strain levels (integral of shear rate with respect to time) using an ad hoc Couette shear cell. Tablets were compressed at different compaction forces using an instrumented compactor simulator, and compaction curves showing the force-displacement profiles during compaction...
09. May 2016
An ultrasound measurement system was employed as a non-destructive method to evaluate its reliability in predicting the tensile strength of tablets and investigate the ben- efits of incorporating it in a continuous line, manufacturing solid dosage forms. Tablets containing lactose, acetaminophen, and magnesium stearate were manufactured contin- uously and in batches. The effect of two processing parameters, compaction force and level of shear strain were examined. Young’s modulus and tensile...
30. March 2016
A pharmaceutical compound was used to study the effect of batch wet granulation process parameters in combination with the residual moisture content remaining after drying on granule and tablet quality attributes. The effect of three batch wet granulation process parameters was evaluated using a multivariate experimental design, with a novel constrained design space. Batches were characterised for moisture content, granule density, crushing strength, porosity, disintegration time and...
21. March 2016
Background: Quince seed mucilage biopolymer (QSMB), famous for ameliorating coughs and controlling asthma symptoms, has not been processed by scientific methods and rules into a local oral tablet. Objectives: The purpose of this study was to investigate and compare the mechanical properties of QSMB with different size fractions of the mucilage powder, dried by oven or by freeze drying, to achieve a tablet. Materials and Methods: The granules dried by oven and freezing processes were classified...
21. February 2016
The aim of this study focus on the extended release formulation on two aspects: the quantification and mechanistic research on pharmaceutical coating curing with a specific focus on how the moisture affect the curing; and in vivo and in vitro release of matrix ER tablets with implications on regulatory biowaiver using marketed products as practical examples. In all cases, it was found that the relative humidity of the environments were more important to reach higher extent of coalescence for EC...
04. February 2016
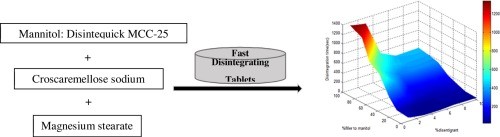
Despite the popularity of orally fast disintegrating tablets (FDTs), their formulation can sometimes be challenging, producing tablets with either poor mechanical properties or high disintegration times. The aim of this research was to enhance the properties of FDTs produced by direct compression to have both sufficient hardness to withstand manual handling, and rapid disintegration time. General multilevel factorial design was applied to optimise and evaluate main and interaction effects of...
02. February 2016
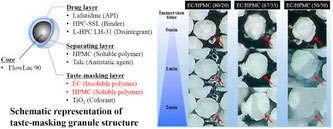
Taste-masking granules were prepared by coating granules with a taste-masking layer prepared by combining the water-insoluble and -soluble polymers, ethylcellulose and hypromellose, respectively. These granules showed an immediate drug release property after a suitable lag time. We confirmed that the dissolution behavior depended on the polymer ratio in the taste-masking layer. The result showed that the dissolution lag time and rate of the taste-masking granules were shortened and enhanced,...