- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
02. October 2018
The production of 3D-printed drugs holds promise for future personalized medicine. Here, we prepared tablets containing naftopidil as a model drug using a semi-solid extrusion-type 3D bioprinter applicable for tissue engineering. A hydrogel is typically used as the printer ink for 3D bioprinters, and we incorporated various amounts of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose hydrogel (30%, 40% and 50% gel) into the printer ink. The resulting 3D-printed gel product was dried to obtain tablets. The...
05. March 2018
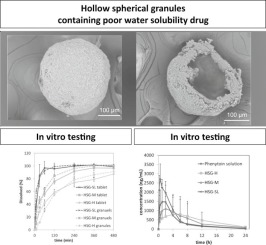
Water-soluble polymers with high viscosity are frequently used in the design of sustained-release formulations of poorly water-soluble drugs to enable complete release of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract. Tablets containing matrix granules with a water-soluble polymer are preferred because tablets are easier to handle and the multiple drug-release units of the matrix granules decreases the influences of the physiological environment on the drug.
26. February 2018
Nine common excipients were examined to determine their ability to cause disproportionation of the HCl salt of a a weakly basic compound. The goal was to determine which excipients were problematic and correlate the results to known properties such as surface pH, slurry pH, or molecular structure. Such a correlation enables a general, simple excipient selection process.
17. February 2018
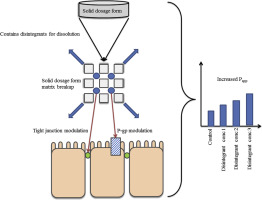
Abstract Pharmaceutical excipients were designed originally to be pharmacologically inert. However, certain excipients were found to have altering effects on drug pharmacodynamics and/or pharmacokinetics. Pharmacokinetic interactions may be caused by modulation of efflux transporter proteins, intercellular tight junctions and/or metabolic enzyme amongst others. In this study, five disintegrants from different chemical classes were evaluated for P-glycoprotein (P-gp) related inhibition and tight...
16. February 2018
Here you find some abstracts of Engineering of "Biomaterials for Drug Delivery Systems - beyond Polyethylene Glycol". 1 – PEGylated “stealth” nanoparticles and liposomes Through nanomedicine, game-changing methods are emerging to deliver drug molecules directly to diseased tissue. The targeted delivery of drugs and imaging agents via drug carrier-based platforms is among the most promising of these methods. Such drug delivery systems can now be synthesized from a wide range of different...
11. December 2017
Nowadays most of the drug substances are coming into the innovation pipeline with poor water solubility. Here, the influence of excipients will play a significant role to improve the dissolution of poorly aqueous soluble compounds. The drug substance needs to be dissolved in gastric fluids to get the better absorption and bioavailability of an orally administered drug. Dissolution is the rate-controlling stage for drugs which controls the rate and degree of absorption.
15. November 2017
The purpose of this study was to explore poly(vinylpyrrolidone-co-vinyl acetate) (PVP VA64) as a novel release-modifier to tailor the drug release from ethylcellulose (EC)-based mini-matrices prepared via hot melt extrusion (HME). Quetiapine fumarate (QF) was selected as model drug. QF/EC/PVP VA64 mini-matrices were extruded with 30% drug loading.
29. August 2017
The main objective of present research investigation is to formulate the Moxi oxacin.HCl Fast Dissolving tablets. Moxi oxacin.HCl, a synthetic u- oroquinolone antibacterial agent, and used to treatacute bacterial sinusitis, acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis
02. May 2017
Highlights
• Binder properties were correlated to granule and tablet properties.
• Groups of binders behave divergent regarding granule and tablet properties.
• Povidone based polymers seem to have another binding behaviour.
• Disintegration of tablets was explained by particle size and viscosity effects.
• Changes in particle size caused larger effects for small-sized binders on tablets.
22. November 2016
Abstract Crospovidone is a commonly used tablet disintegrant. However, the synthetic disintegrant has been known to be hygroscopic and high moisture content in crospovidone used could exert deleterious effects on tablets formulated with it. The objective of this study was to elicit a better understanding between crospovidone-water interaction and its effect on disintegrant performance. Moisture sorption and desorption isotherms were obtained together with the enthalpy of immersion. Crospovidone...