- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
21. September 2018
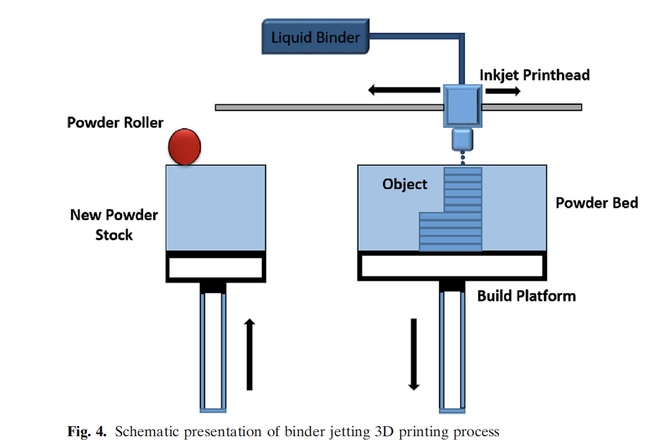
Three-dimensional (3D) printing was discovered in the 1980s, and many industries have embraced it, but the pharmaceutical industry is slow or reluctant to adopt it. Spiritam® is the first and only 3D-printed drug product approved by FDA in 2015. Since then, the FDA has not approved any 3D-printed drug product due to technical and regulatory issues. The 3D printing process cannot compete with well-established and understood conventional processes for making solid dosage forms. However,...
20. July 2018
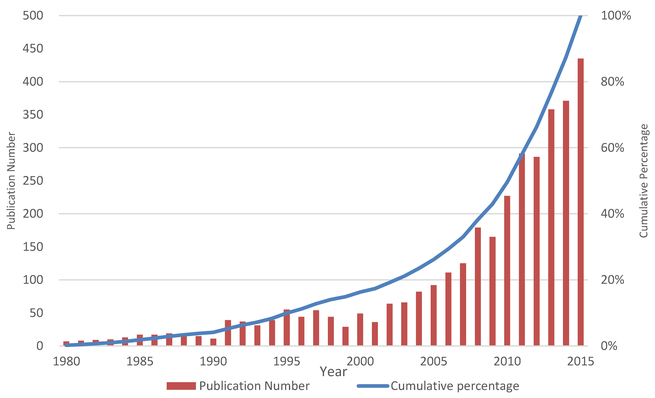
Solid dispersions are an effective formulation technique to improve the solubility, dissolution rate, and bioavailability of water-insoluble drugs for oral delivery. In the last 15 years, increased attention was focused on this technology. There were 23 marketed drugs prepared by solid dispersion techniques. Objective: This study aimed to report the big picture of solid dispersion research from 1980 to 2015. Method: Scientific knowledge mapping tools were used for the qualitative and the...
11. January 2018
The object of this study is to prepare and evaluate tablets with predesigned internal scaffold structure using 3D printing to achieve sustained drug release. Model drug (ibuprofen) and sustained release material (ethyl cellulose), together with other excipients, were firstly mixed and extruded into filaments by hot melt extrusion. Then these obtained filaments were printed into tablets by fused deposition modeling.
09. January 2018
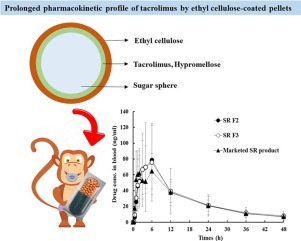
A novel once-a-day sustained-release (SR) system of tacrolimus (FK506), a poorly water-soluble immunosuppressive agent, was designed employing ethyl cellulose (EC) polymer as release retardant. Drug (5 mg) was layered onto sugar spheres (518.3 mg) with hypromellose (5 mg), to transform the drug from a crystalline to an amorphous form.
26. December 2017
Micro sponge is a novel approach for targeting the drug to the colon for the management of colon ailments such as inflammatory bowel disease. Prednisolone loaded microsponges (PLMs) were prepared and coated with Eudragit S 100 (ES) and evaluated for colon specific drug delivery.
13. November 2017
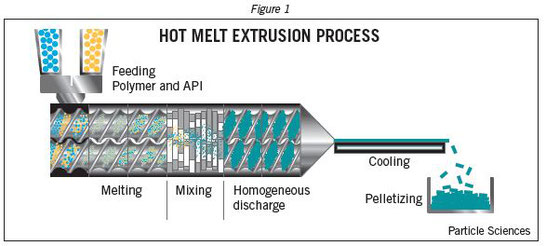
Amorphous solid dispersions (SDs) are considered as one of the most effective strategies for the formulation of poorly water-soluble compounds. The active compound is dispersed in an inert carrier composed of a polymer and active excipients. Since the drug is amorphous, there is typically an increase in apparent solubility as well as dissolution rate. Various methods are employed for manufacturing of SDs, nevertheless, hot-melt extrusion (HME) has become one of the most common process techniques
10. November 2017
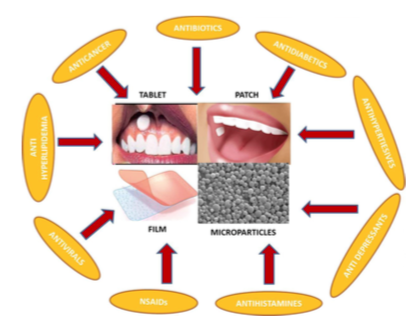
Mucoadhesive formulations are well known for the delivery of drugs via the mucosal membrane of oral (sub- lingual, buccal and gingival), rectum, nose, eyes, and vagi- na. Among the various drug delivery approaches, the buc- cal mucosa delivery system o ers several bene ts like easy accessibility, patient compliance, a relatively large surface area of absorption for drug molecules, reduced gastric ir- ritation and simple delivery devices.
12. October 2017
The current study was designed for preparation of gastro-retentive floating tablet of ranitidine HCl by using polymers ethyl cellulose (EC) and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and xanthan gum (XG) in an attempt to delay its gastric retention time. The tablets were manufactured by direct compression technique. The outcome of varying concentrations of HPMC, XG and EC on drug release was evaluated.