- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
08. November 2017
Colon delivery systems for oral administration have grown in popularity since the 1990s, primarily because of the increasing incidence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that has broadly been demonstrated to benefit from topical pharma- cological treatment.
15. December 2016
Abstract Predictive in vitro test methods addressing the parameters relevant to drug release in the pediatric gastrointestinal tract could be an appropriate means for reducing the number of in vivo studies in children. However, dissolution models addressing the particular features of pediatric gastrointestinal physiology and typical pediatric dosing scenarios have not yet been described. The objective of the present study was to combine the knowledge on common vehicle types and properties and...
22. November 2016
Abstract Gastrointestinal drug administration is the preferred route for the majority of drugs however, the natural physiology and physicochemistry of the gastrointestinal tract is critical to absorption but complex and influenced by factors such as diet or disease. The pharmaceutical sciences drive for product consistency has led to the development of in vitro product performance tests whose utility and interpretation is hindered by the complexity, variability and a lack of understanding. This...
17. November 2016
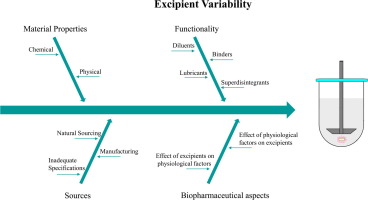
Abstract Implementation of Quality by Design approaches in pharmaceutical industry requires a sound understanding of the parameters triggering final product variability. Excipients, although generally regarded as inert components, are of great significance in terms of solid dosage form development and any variation in the material attributes may impact drug product performance. Sourcing, production and processing are contributing factors to excipient variability. Interchange between different...
08. August 2016
Abstract Supersaturating drug delivery systems can enhance the oral bioavailability of poorly soluble drug compounds. Supersaturation of such compounds has been studied in many different ways; however, a more standardized method is required. The rationale of choosing suitable concentrations of supersaturation to study has previously been very inconsistent. This makes comparisons between studies and compounds difficult, as the propensity of compounds to supersaturate varies greatly. This study...
07. July 2016
Abstract An in vitro biorelevant gastrointestinal transfer (BioGIT) system was assessed for its ability to mimic recently reported albendazole concentrations in human upper small intestine after administration of free base suspensions to fasted adults in absence and in presence of supersaturation promoting excipients (hydroxypropylmethylcellulose and lipid self-emulsifying vehicles). The in vitro method was also used to evaluate the likely impact of using the sulfate salt on albendazole...
06. May 2016
The main goal of any drug delivery system is to achieve desired concentration of the drug in blood or tissue, which is therapeutically effective and nontoxic for a prolonged period. Various attempts have been made to develop gastroretentive delivery systems such as high density system, swelling, floating system. The recent developments of FDDS including the physiological and formulation variables affecting gastric retention, approaches to design single-unit and multiple-unit floating systems,...
01. February 2016
We aimed to develop a suitable micropellet delivery system for Lansoprazole, a highly potent proton pump inhibitor and acid-unstable physiologically active anti-secretory compound. Although clinically manifested to be highly effective for treating acid reux-related diseases, poor water solubility and short gastric retention time, typically does not provide extended period of relief. Materials and method: Micropellets of the drug was prepared using ionotropic gelation technique, where gelation...