- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
02. October 2018
The production of 3D-printed drugs holds promise for future personalized medicine. Here, we prepared tablets containing naftopidil as a model drug using a semi-solid extrusion-type 3D bioprinter applicable for tissue engineering. A hydrogel is typically used as the printer ink for 3D bioprinters, and we incorporated various amounts of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose hydrogel (30%, 40% and 50% gel) into the printer ink. The resulting 3D-printed gel product was dried to obtain tablets. The...
16. August 2018
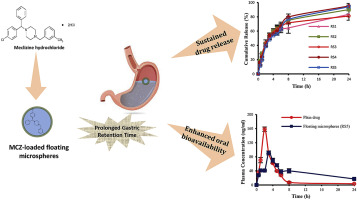
The aim of this study was to investigate whether floating microspheres prepared from polymer blends of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose in combination with either Eudragit S100 or Eudragit RS100 could improve the systemic bioavailability of the antiemetic drug; meclizine HCl (MCZ). Floating microspheres containing MCZ were prepared by emulsion solvent evaporation method. The influence of different polymer blend compositions on various formulation parameters and in vitro release characteristics of...
08. May 2018
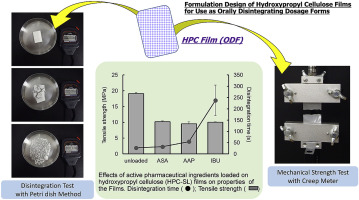
Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) is a water-soluble polymer used as a binder during pharmaceutical tableting and granulation. HPC is also known as a base material for pharmaceutical film by virtue of its film formability with excellent plasticity. The aim of this study was to assess the applicability of HPC to orally disintegrating film (ODF) and to investigate optimization of the ODF formulation of HPC. The effects of the molecular weight of HPC and the addition of active pharmaceutical...
06. May 2018
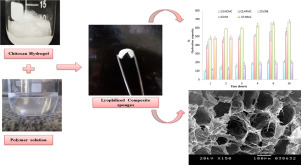
In the course of application and modernization of buccal dosage forms, lyophilized sponges for transmucosal drug delivery symbolize one of the most attractive approaches. Chitosan (CS) has been extensively investigated as a forming material of different buccal dosage forms including sponges. However, CS-based buccal delivery systems suffer from many limitations like weak adhesion strength and poor tensile properties. So, for the first time, the current study focused on the polymer blending...
05. March 2018
This study presents a framework for process and product development on a continuous direct compression manufacturing platform. A challenging sustained release formulation with high content of a poorly flowing low density drug was selected. Two HPMC grades were evaluated as matrix former: standard Methocel CR and directly compressible Methocel DC2. The feeding behavior of each formulation component was investigated by deriving feed factor profiles.
01. March 2018
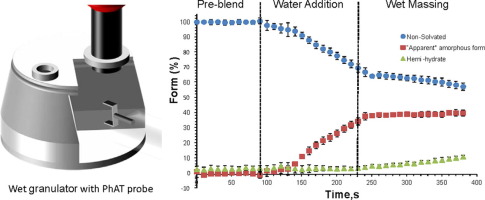
Form changes during drug product processing can be a risk to the final product quality in terms of chemical stability and bioavailability. In this study, online Raman spectroscopy was used to monitor the form changes in real time during high shear wet granulation of Compound A, a highly soluble drug present at a high drug load in an extended release formulation. The effect of water content, temperature, wet massing time and drying technique on the degree of drug transformation were examined.
11. January 2018
The oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) can be improved by the preparation of amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) where the API is dissolved in polymeric excipients. Desired properties of such ASDs like storage stability, dissolution behavior, and processability can be optimized by additional excipients. In this work, the influence of so-called low-molecular-weight excipients (LMWEs) on the phase behavior of ASDs was investigated.
18. October 2017
In the drug delivery area, versatile therapeutic systems intended to yield customized combinations of drugs, drug doses and release kinetics have drawn increasing attention, especially because of the advantages that personalized pharmaceutical treatments would offer.
20. September 2017
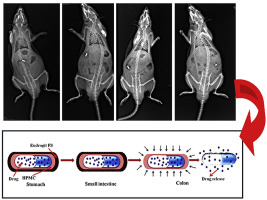
Abstract The objective of this study was to evaluate the combination of pH-dependent and time-dependent polymers on drug release in order to optimize coating for colonic delivery. Response surface methodology (RSM) based on central composite design (CCD) was employed for formulation optimization. Theophylline was used as model drug and Eudragit® FS 30D and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) were used as pH-dependent and time-dependent polymer, respectively. Dissolution test was carried out...
19. April 2017
Abstract The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of the different physiological parameters of the gastrointestinal (GI) fluid (pH, buffer capacity, and ionic strength) on the in vitro release of the weakly basic BCS class II drug quetiapine fumarate (QF) from two once-a-day matrix tablet formulations (F1 and F2) developed as potential generic equivalents to Seroquel® XR. F1 tablets were prepared using blends of high and low viscosity grades of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose...