- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
26. September 2018
The increasing number of poorly water-soluble drug candidates in pharmaceutical development is a major challenge. Enabling techniques such as amorphization of the crystalline drug can result in supersaturation with respect to the thermodynamically most stable form of the drug, thereby possibly increasing its bioavailability after oral administration. The ease with which such crystalline drugs can be amorphized is known as their glass forming ability (GFA) and is commonly described by the...
18. January 2018
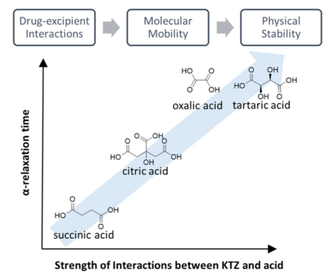
The use of excipients other than polymers for enhancing the physical stability of amorphous active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) has largely been unexplored. We investigated several organic acids (oxalic, tartaric, citric and succinic acid) for the purpose of stabilizing a weakly basic API, ketoconazole (KTZ), in the amorphous state.
05. December 2017
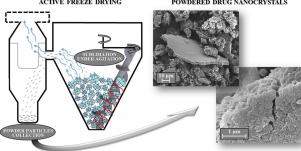
Active Freeze Drying allows for producing lyophilised powders by progressive agitation of frozen blocks undergoing sublimation. One potential application of this process is the formulation design of unstable nanosuspensions for oral drug delivery, as here shown for nanocrystal-based ketoconazole powder.
02. August 2017
The patient receives a pharmaceutical product, not a drug. The pharmaceutical products are formulated with a drug, an active ingredient to produce the maximum therapeutic effect after oral absorption.
15. June 2016
Purpose To identify the key formulation factors controlling the initial drug and polymer dissolution rates from an amorphous solid dispersion (ASD). Methods Ketoconazole (KTZ) ASDs using PVP, PVP-VA, HMPC, or HPMC-AS as polymeric matrix were prepared. For each drug-polymer system, two types of formulations with the same composition were prepared: 1. Spray dried dispersion (SDD) that is homogenous at molecular level, 2. Physical blend of SDD (80% drug loading) and pure polymer (SDD-PB) that is...
23. February 2016
The aim of this study was firstly to evaluate the utility of Hybrane S1200 as a hot melt extrusion (HME) carrier to prepare instant-release multiparticulate systems for very poorly-soluble drugs such as ketoconazole or nifedipine. Hybrane S1200 allows an easy extrusion of its drug mixtures at a relatively low temperature, not higher than 90 °C, and with no need of any additional aid. Extrudates containing 10% of nifedipine or ketoconazole form monophasic systems. Nifedipine extrudate shows no...