- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
04. September 2018
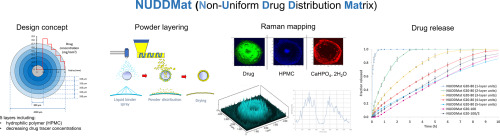
A decrease in the release rate over time is typically encountered when dealing with hydrophilic matrix systems for oral prolonged release due to progressive increase of the distance the drugmolecules have to cover to diffuse outwards and reduction of the area of the glassy matrix at the swelling front. In order to solve this issue, a novel formulation approach based on non-uniformdistribution of the active ingredient throughout the swellable polymer matrix was proposed and evaluated. Various...
18. August 2018
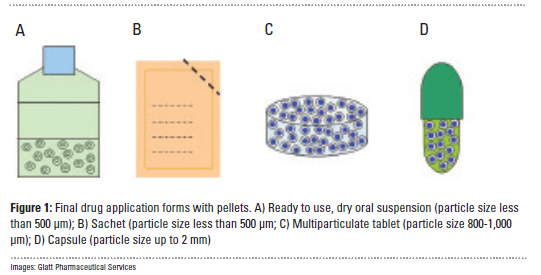
In contrast to classic single-unit dosage forms such as tablets, the dosage of the drug substance in multi-particulate systems is divided on a plurality of subunits – typically consisting of thousands of spherical pellet particles with a diameter of between 100 and 2,000 μm. This means that non-disintegrating, monolithic single-unit forms retain their structure in the digestive tract, whereas the multi-particular preparations consist of numerous sub-units which disperse after administration....
05. September 2017
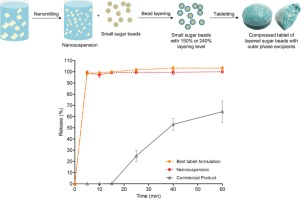
Abstract There has been limited research done on the downstream processing of nanosuspensions into solid oral dosage forms. This paper demonstrates the bead layering process with a layering level at 150% and 240%, as well as the selection and justification of the outer phase excipients for tabletability and disintegrating properties. In a previous study, an itraconazole nanosuspension stabilised by SDS and HPMC E5 was layered onto sugar beads with coating polymer HPMC VLV. In the current study,...
18. April 2017
Abstract There is more research required to broaden the knowledge on the downstream processing of nanosuspensions into solid oral dosage forms, especially for coated nanosuspensions onto beads as carriers. This study focuses on bead layering as one approach to solidify nanosuspensions. The aim was to systematically investigate the influence of type of coating polymer (HPMC VLV vs. copovidone), bead material and bead size (sugar vs. MCC, and small vs. large) and coating thickness (50%–150%...
24. August 2016
ABSTRACT In pharmaceutical industries, pellets are multiparticulate dosage form which was formed by the agglomeration of fine powdered excipient and drugs together that leads to the formation of small free flowing spherical or semi spherical particles. This technique is called as pelletization process. Pellets are typically varied between 500-1500 μm in size for pharmaceutical applications. It is of great interest over other similar techniques due to its uniformity of dose, less susceptibility...
04. July 2016
Abstract We aimed to elucidate the mechanism of the spheronization of pharmaceutical material crystals through extremely high shearing force using a mechanical powder processor, which produces spherical crystals without a solvent. The spheronization of theophylline, acetaminophen, clarithromycin, ascorbic acid and lactose was investigated, and the relationship between the spheronization mechanism and material characteristics was also examined. Theophylline and ascorbic acid crystals were...
25. January 2016
Gastro-resistant pellets were prepared by use of three different drug loading techniques (powder layering, solution layering and suspension layering) and two different enteric coating techniques (powder layering and suspension layering). Pellets produced by different layering techniques were compared in terms of morphological characteristcs, content of drug, release properties and stability. More
19. December 2015
The aim of the research was to investigate the complete process of pellet production in a Wurster fluidized bed coater in order to determine the main factors affecting the migration phenomenon of a soluble API through the ethycellulose film coating (Surelease®) and hence the long-term stability of the controlled release pellets. Guaifenesin (GFN), as BCS class I model drug, was layered on sugar spheres using a binder-polymer solution containing the dissolved GFN. The drug loaded pellets were...
17. November 2015
Urea cycle disorders are a group of inherited orphan diseases leading to hyperammonemia. Current therapeutic strategy includes high doses of sodium benzoate leading to three or four oral intakes per day. As this drug is currently available in capsules or in solution, children are either unable to swallow the capsule or reluctant to take the drug due to its strong bitter taste. More
16. November 2015
Flurbiprofen is a slightly water soluble, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory active ingredient with analgesic and antipyretic activity. The purpose of this study was to develop an appropriate pellet production method for pH independent sustained release pellet formulation of flurbiprofen. Flurbiprofen pellets were produced by three different production methods; Suspension Layering, Extrusion Spherization, Rotagranulation. Although the simple and fast processing properties of Extrusion...