- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
11. April 2017
Abstract Ribavirin (C8H12N4O5; anti-viral agent) was crystallized as two unique, phase-pure polymorphs (R-I and R-II). Calorimetrically determined isobaric heat capacities and heat of transition data were utilized to determine the solid-state transition temperature (Ttr), confirming enantiotropism, while R-I was determined to be kinetically stable at ambient temperature. Unprocessed samples of the low Tm polymorph, R-II, did not convert into R-I when held isothermally well above Ttr for 7 days....
08. November 2016
Abstract Drug release from hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) hydrophilic matrix tablets is controlled by drug diffusion through the gel layer of the matrix-forming polymer upon hydration, matrix erosion, or combination of diffusion and erosion mechanisms. In this study, the relationship between viscoelastic properties of the gel layer of swollen intact matrix tablets and drug release was investigated. Two sets of quetiapine fumarate (QF) matrix tablets were prepared using the high viscosity...
25. June 2016
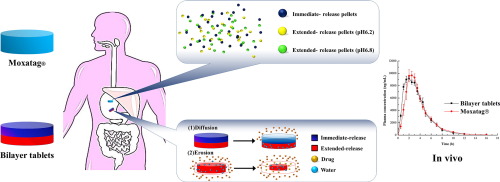
Abstract Multilayer/bilayer tablets have been applied for the formulation of incompatible components for compound preparations, but more often they are used to modify drug release. The objective of this study was to explore the feasibility of developing, using a bilayer tablet strategy, an immediate- and extended-release formulation of amoxicillin. The formulation of each layer was optimized separately and the bilayer tablets were compressed at an immediate/extended layer weight ratio of 3:7....
19. January 2016
This paper deals with a study of the novel coprocessed dry binder Combilac®, which contains 70% of α-lactose monohydrate, 20% of microcrystalline cellulose and 10% of native corn starch. These tests include flow properties, compressibility, lubricant sensitivity, tensile strength and disintegration time of tablets. Compressibility is evaluated by means of the energy profile of compression process, test of stress relaxation and tablet strength. More
24. September 2015
Carvedilol (CARV) is a widely used non-selective β-blocker, which has shown low bioavailability after oral administration (20 %) due to its low water solubility and intense first-pass metabolism. Lipid-based drug delivery systems have been proposed to improve CARV oral bioavailability. An evaluation of drug–excipient compatibility is needed to clarify potential physical and chemical interactions between them and therefore guarantee a correct selection of excipients. More