- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
17. July 2018
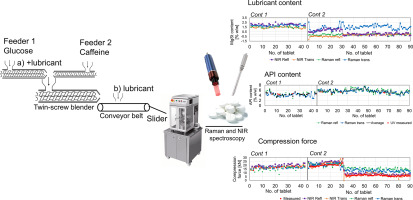
By the advent of continuous pharmaceutical manufacturing, fast and accurate characterization of product quality has become of a major interest. Although it also promotes the real-time release testing approach, so far mainly content uniformity studies were performed by near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy. This paper proposes the simultaneous application of NIR and Raman spectroscopy to nondestructively analyze the critical quality attributes of continuously produced tablets in a real-time release...
26. May 2018
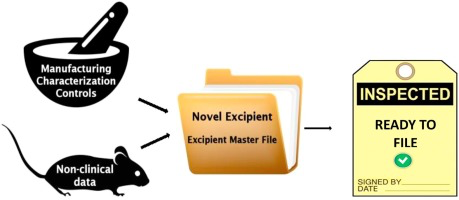
Novel excipients are indispensable in development of modern, advanced drug delivery systems and biotechnology-derived drugs. Although numerous novel excipients are developed for pharmaceutical use, they are not frequently seen in medicinal products due to the strict regulatory requirements and perception that their use makes new product evaluation more complex with risk of delays in the approval process. Regulators regard novel excipients as new substances and whenever new excipient is used in...
05. July 2016
Pecuniary gain, when stretched past the altruistic; carried through the protestant means to salvation and, past Adam Smith’s ‘hidden hand’ hypothesis; usually ends up at the other extreme of Hobbesian callousness, as portrayed by Orson Welles’ penicillin diluting character in The Third man. In light of the Volkswagen scandal, where software was surreptitiously installed to generate false, in-specification, results when the automobile was tested for emissions, it is prudent to examine...
25. June 2016
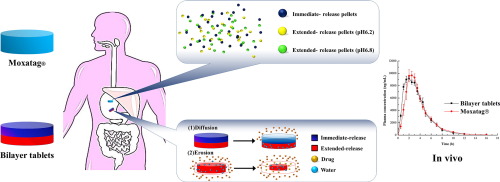
Abstract Multilayer/bilayer tablets have been applied for the formulation of incompatible components for compound preparations, but more often they are used to modify drug release. The objective of this study was to explore the feasibility of developing, using a bilayer tablet strategy, an immediate- and extended-release formulation of amoxicillin. The formulation of each layer was optimized separately and the bilayer tablets were compressed at an immediate/extended layer weight ratio of 3:7....
21. June 2016
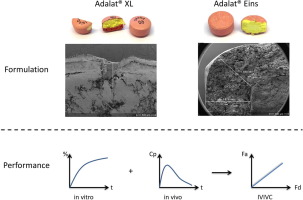
Aims Food intake is known to have various effects on gastrointestinal luminal conditions in terms of transit times, hydrodynamic forces and/or luminal fluid composition and can therefore affect the dissolution behavior of solid oral dosage forms. The aim of this study was to investigate and detect the dosage form-dependent food effect that has been observed for two extended-release formulations of nifedipine using in vitro dissolution tests. Methods Two monolithic extended release formulations,...
02. March 2016
In the development of orally inhaled and nasal products (OINDPs), a primary focus is achieving deposition at the preferred site within the pulmonary system or nasal cavity. The particle size or droplet size of the delivered drug has a strong influence on this aspect of performance, explaining the reliance on particle size measurement within OINDP research. However, as OINDP performance is refined, more attention is being paid to the path of the drug molecule following deposition. The speed of...
04. January 2016
01. November 2015
Highlights Development of a new biorelevant dissolution method for orodispersible films, considering mechanical force, saliva flow, volume and composition. Comparison of different conventional methods and the new biorelevant dissolution method regarding their consideration of in vivo conditions. Feasibility and problems of different dissolution setups for orodispersible films. Conventional dissolution setups show faster concentration onset compared to the new developed biorelevant setup. The...
24. September 2015
Carvedilol (CARV) is a widely used non-selective β-blocker, which has shown low bioavailability after oral administration (20 %) due to its low water solubility and intense first-pass metabolism. Lipid-based drug delivery systems have been proposed to improve CARV oral bioavailability. An evaluation of drug–excipient compatibility is needed to clarify potential physical and chemical interactions between them and therefore guarantee a correct selection of excipients. More
14. August 2015
Manufacturers of excipients are being sent inappropriate requests for stability data by some regulators and pharma companies, threatening to disrupt the supply chain, IPEC claims. More