- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
26. September 2018
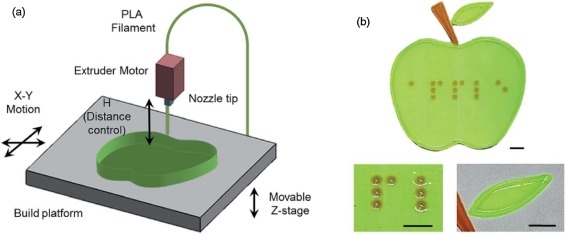
Three-dimensional (3D) printing is classified as a revolutionary, disruptive manufacturing technology. Cellulose (the most abundant natural polymer) and its many derivatives have been widely studied for many applications. The combination of 3D printing with cellulose-based feedstocks is therefore of critical interest. This review highlights many studies on 3D printing applications of plant-derived cellulose and its derivatives. Potential materials include cellulose ethers/esters,...
13. August 2018
The aim of this study is to determine favorable process conditions for the coating of placebo tablets. Tablets made of microcrystalline cellulose are coated with hydroxypropyl cellulose polymer and Advantia™ Prime polymeric mixture film in lab-scale fluid-bed environment with a Wurster tube. In order to determine favorable process conditions (concentration, Wurster tube position, inlet air temperature, and atomization pressure), evaluation factors expressing process efficiency were...
08. July 2018
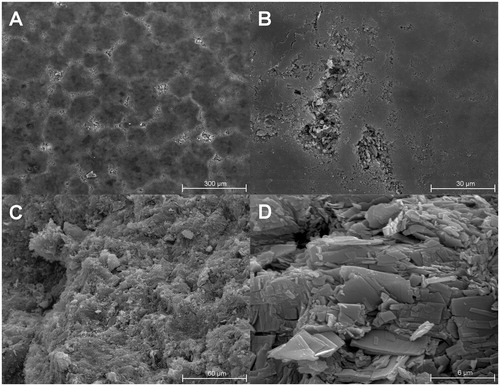
Tricalcium citrate (TCC) was characterized as a tableting excipient for direct compression (DC) and dry granulation (DG). Significance: Brittle materials usually lead to tablets of inferior mechanical strength compared to plastic deforming materials. A brittle material exhibiting a high tabletability with the ability to retain that behavior during recompression would represent a valuable alternative to the commonly used microcrystalline cellulose. Methods: Tablets of TCC and other common...
20. June 2018
Itraconazole is a fungicide drug which has low bioavailability due to its poor water solubility. Amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) is a tool that has the potential to greatly increase the dissolution rate and extent of compounds. In this work, the dissolution of tablets containing the ASD of itraconazole with either hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) or vinylpyrrolidone-vinyl acetate copolymer (PVPVA) was compared in order to find a formulation which can prevent the drug from the precipitation...
12. May 2018
The objective of this study was to evaluate non-crystalline cellulose (NCC) as a novel tablet excipient in solid oral dosage forms in comparison with microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) and silicified microcrystalline cellulose (Prosolv®, SMCC). Significance: MCC, although a widely used tablet excipient, has diasdvantages in terms of its low dilution potential for potent drugs, and sensitivity to lubricant and moisture. SMCC, a modified version of MCC, has improved tablet compression properties....
10. May 2018
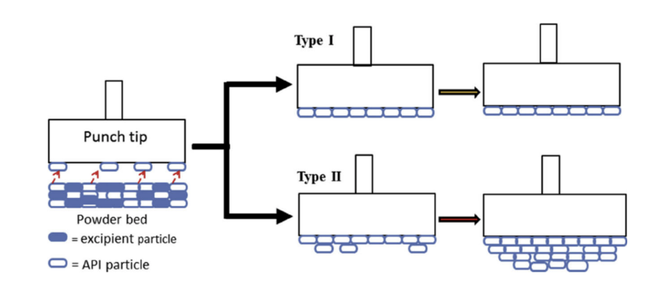
Purpose To investigate how excipient matrix affects punch sticking propensity of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API), with the focus on the effect of bonding interactions between API-API (F2) and API-excipient (F3). Method Sticking kinetics of direct compression formulations, consisting of 20% of celecoxib (CEL) or ibuprofen (IBN) indifferent excipient matrices, i. e., microcrystalline cellulose (Avice l PH102 and Avicel PH105 dry coated with nano-sized silica (PH105(n)), hypromellose (K15...
09. April 2018
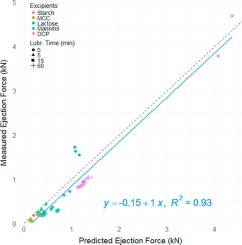
Pharmaceutical powders can exhibit markedly different tablet ejection forces. The purpose of this study is to understand the factors leading to the variability of the tablet ejection force and its sensitivity to lubrication. The study showed that the tablet ejection force is mainly governed by 1) tablet diameter and thickness, 2) compact-die wall friction coefficient, and 3) residual die wall stress upon ejection; the latter was further controlled by the maximum compression pressure, as well as...
22. March 2018
The Glatt CPS® Technology (Complex Perfect Spheres) is a fluid bed rotor technology for producing spherical matrix pellets with a smooth surface and high density. Typically, microcrystalline cellulose is used as a basic excipient for pelletization using the CPS® Technology [1]. In the past extensive studies using soluble APIs (active pharmaceutical ingredient) as Metoprolol succinate [2] and Propranolol hydrochloride [3] were performed. During this study matrix pellets containing an insoluble...
17. March 2018
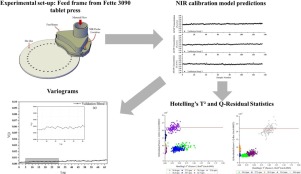
Near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy was used to determine the drug concentration in 3% (w/w) acetaminophen blends within the complex flow regime of the tablet press feed frame just before tablet compaction. NIR spectra also provided valuable information on the powder flow behavior within the feed frame and were used to track when a process enters or leaves the steady state.
16. March 2018
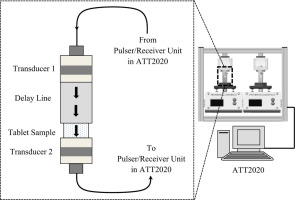
Currently, the compressed tablet and its oral administration is the most popular drug delivery modality in medicine. The accurate porosity and tensile strength characterization of a tablet design is vital for predicting its performance such as disintegration, dissolution, and drug-release efficiency upon administration as well as ensuring its mechanical integrity.